Genetic counseling practice based competencies are fundamental to the effective delivery of genetic services. They encompass the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that genetic counselors need to provide high-quality care to individuals and families affected by genetic conditions.
This article explores the core competencies required for genetic counseling practice, including knowledge of genetics, communication and interpersonal skills, ethical and legal considerations, and the role of genetic counselors in healthcare. It also highlights the importance of education, training, and professional development for genetic counselors.
1. Knowledge and Skills Required for Genetic Counseling Practice
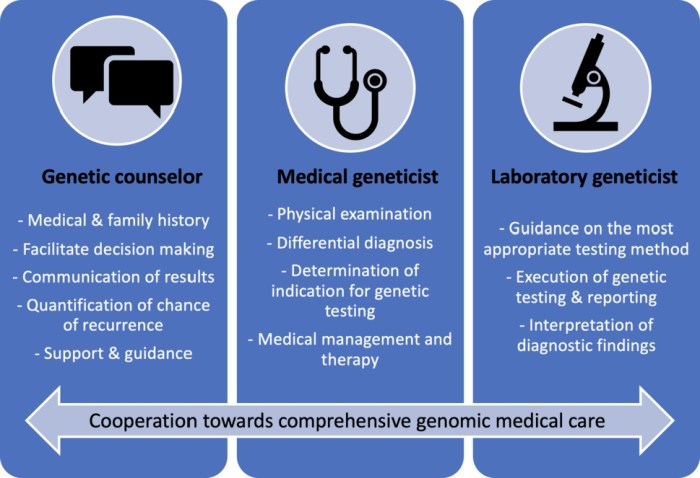
Genetic counselors require a comprehensive knowledge base and specialized skills to effectively practice. They must possess a deep understanding of human genetics, including inheritance patterns, genetic disorders, and the impact of genetic variations on health. Additionally, they need expertise in counseling techniques, communication, and interpersonal skills to effectively interact with patients and families.
Core Knowledge
- Human genetics
- Medical genetics
- Genomics
- Bioinformatics
- Genetic testing and interpretation
Essential Skills
- Counseling skills
- Communication skills
- Interpersonal skills
- Problem-solving skills
- Critical thinking skills
- Ethical decision-making skills
- Cultural sensitivity
2. Communication and Interpersonal Skills in Genetic Counseling
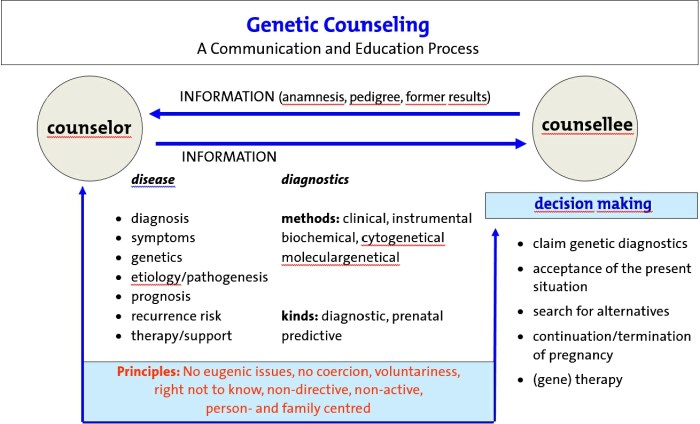
Effective communication is paramount in genetic counseling. Genetic counselors must be able to convey complex genetic information in a clear and understandable manner to patients and families. They utilize various communication techniques, such as active listening, empathy, and non-verbal cues, to create a supportive and informative environment.
Challenges in Communicating Genetic Information
- Technical and complex nature of genetic information
- Emotional impact of genetic information on patients and families
- Cultural and linguistic barriers
- Limited health literacy
3. Ethical and Legal Considerations in Genetic Counseling

Genetic counselors must adhere to strict ethical and legal guidelines to ensure the responsible and ethical practice of genetic counseling. They are obligated to protect patient privacy, confidentiality, and autonomy. Additionally, they must be aware of and comply with relevant laws and regulations governing genetic testing and counseling.
Ethical Considerations
- Patient autonomy and informed consent
- Privacy and confidentiality
- Non-discrimination
- Beneficence and non-maleficence
- Justice and equity
Legal Considerations, Genetic counseling practice based competencies
- Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
Top FAQs: Genetic Counseling Practice Based Competencies
What are the core competencies required for genetic counseling practice?
The core competencies for genetic counseling practice include knowledge of genetics, communication and interpersonal skills, ethical and legal considerations, and the role of genetic counselors in healthcare.
How do genetic counselors ensure that they are practicing ethically and legally?
Genetic counselors ensure ethical and legal practice by adhering to professional guidelines, maintaining confidentiality, obtaining informed consent, and respecting patient autonomy.
What is the role of genetic counselors in healthcare?
Genetic counselors play a vital role in healthcare by providing information and support to individuals and families affected by genetic conditions. They collaborate with other healthcare professionals to improve patient outcomes and advance the field of genetic medicine.
