Which statement about anorexia nervosa is true? This question sparks a journey into the complexities of a severe eating disorder that captivates attention and demands a nuanced understanding. anorexia nervosa is a relentless battle against self, fueled by a distorted body image and an unrelenting pursuit of thinness.
As we delve into its depths, we will uncover the truth behind common misconceptions, unravel the contributing factors, and explore the challenges and triumphs of recovery.
Delving into the realm of anorexia nervosa, we uncover a labyrinth of psychological, biological, and social factors that intertwine to shape its development. Genetic predispositions, personality traits, and family dynamics weave a tapestry of risk, while societal pressures and cultural ideals can further fuel the disorder’s grip.
Understanding these intricate connections is paramount in unraveling the complexities of anorexia nervosa.
Definition and Overview: Which Statement About Anorexia Nervosa Is True
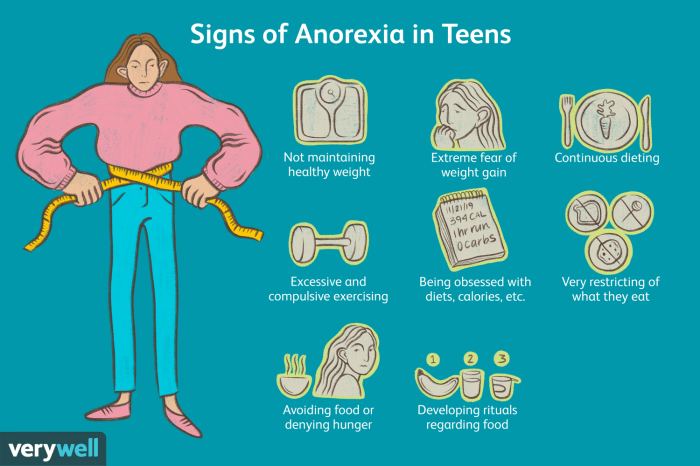
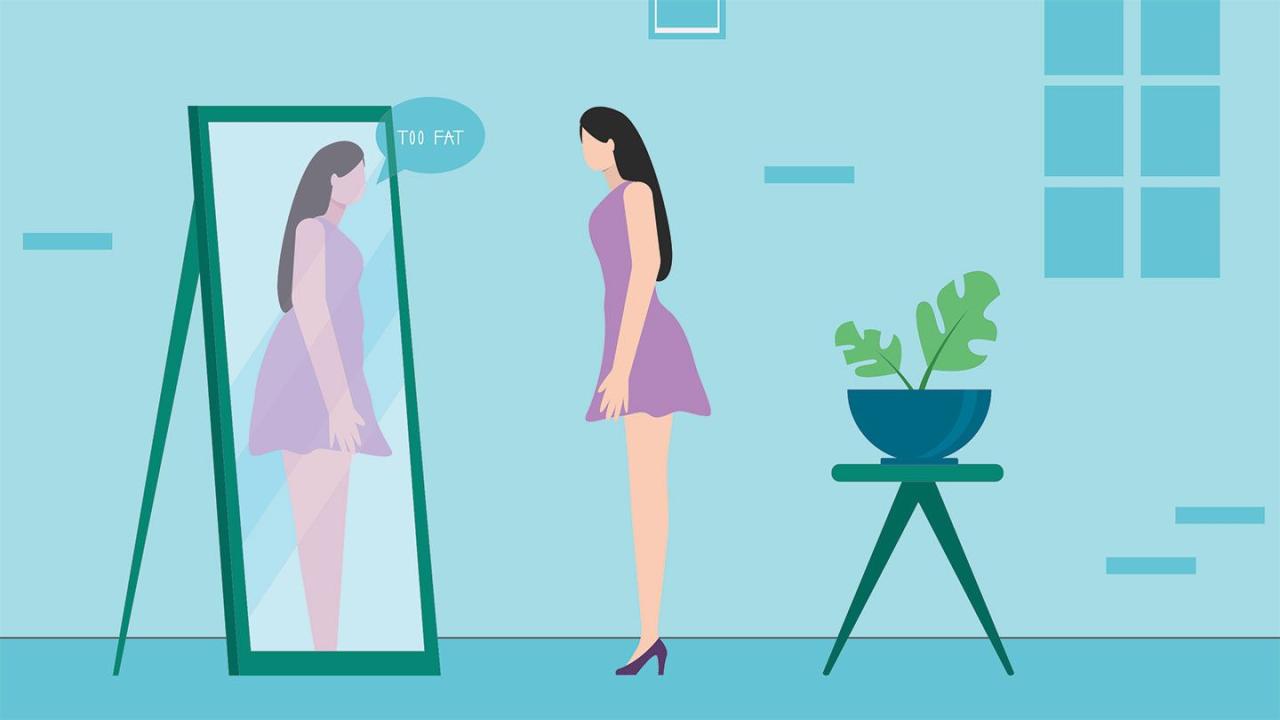
Anorexia nervosa is a severe eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight, a distorted body image, and extreme food restriction. It primarily affects adolescent girls and young women, but it can also occur in males and individuals of other age groups.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the diagnostic criteria for anorexia nervosa include:
- Restriction of energy intake relative to requirements, leading to significantly low body weight
- An intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat, even when underweight
- A disturbance in the way one’s body weight or shape is experienced, with an excessive influence on self-worth
Causes and Risk Factors, Which statement about anorexia nervosa is true
The exact cause of anorexia nervosa is unknown, but it is believed to result from a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors.
Biological factors may include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Neurochemical imbalances
- Hormonal dysregulation
Psychological factors may include:
- Low self-esteem
- Perfectionism
- Anxiety disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Social factors may include:
- Cultural pressure to be thin
- Family history of eating disorders
- Peer pressure
Symptoms and Complications
Anorexia nervosa can manifest in various physical, psychological, and behavioral symptoms.
Physical symptoms may include:
- Extreme weight loss
- Amenorrhea (loss of menstrual periods)
- Dry skin and hair
- Brittle nails
- Lanugo (fine body hair)
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Osteoporosis
Psychological symptoms may include:
- Distorted body image
- Intense fear of gaining weight
- Low self-esteem
- Depression
- Anxiety
Behavioral symptoms may include:
- Excessive exercise
- Food restriction
- Purging behaviors (e.g., vomiting, laxative use)
- Social withdrawal
- Substance abuse
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment for anorexia nervosa typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Psychotherapy (e.g., cognitive-behavioral therapy, family therapy)
- Medication (e.g., antidepressants, antipsychotics)
- Nutritional rehabilitation
- Medical monitoring
Recovery from anorexia nervosa can be challenging and often requires long-term support and monitoring. The goal of treatment is to restore a healthy weight, address underlying psychological issues, and prevent relapse.
Essential Questionnaire
Is anorexia nervosa a choice?
No, anorexia nervosa is not a choice. It is a severe mental illness characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted body image.
What are the warning signs of anorexia nervosa?
Warning signs of anorexia nervosa include extreme weight loss, excessive exercise, preoccupation with food and weight, and a distorted body image.
What are the long-term health consequences of anorexia nervosa?
Anorexia nervosa can lead to a range of serious health consequences, including malnutrition, organ damage, and even death.