With Punnett squares x-linked answer key at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Introduction to Punnett Squares
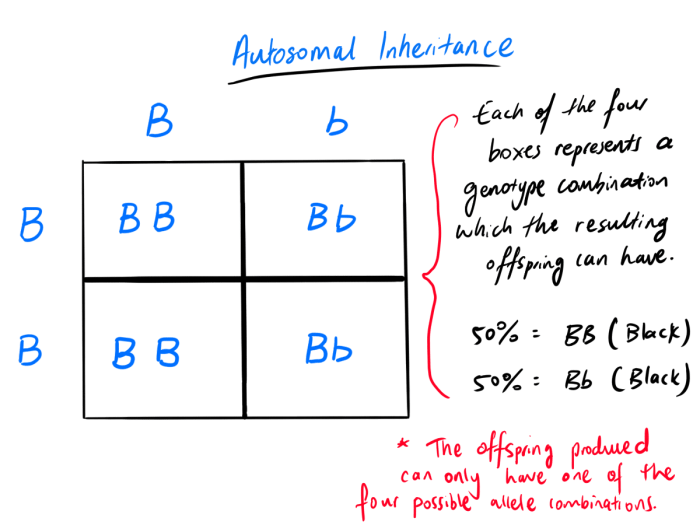
Punnett squares are a graphical tool used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross. They are named after Reginald Punnett, a British geneticist who first described them in 1905.Punnett squares are based on the principles of Mendelian inheritance, which state that each individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent.
The alleles can be either dominant or recessive. A dominant allele is expressed in the phenotype of the individual even if it is only present in one copy. A recessive allele is only expressed in the phenotype if it is present in two copies.Punnett
squares are used to predict the probability of an offspring inheriting a particular combination of alleles. This information can be used to predict the phenotype of the offspring, as well as the likelihood of the offspring inheriting a particular genetic disorder.
Using Punnett Squares
To use a Punnett square, the first step is to determine the genotypes of the parents. The genotypes of the parents are then written along the top and side of the square. The next step is to fill in the square with the possible combinations of alleles that the offspring can inherit.
The alleles that are inherited from the mother are written in the rows of the square, and the alleles that are inherited from the father are written in the columns of the square.The final step is to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
The genotypes of the offspring are determined by the combination of alleles that they inherit from their parents. The phenotypes of the offspring are determined by the expression of the dominant and recessive alleles in their genotypes.
X-Linked Inheritance: Punnett Squares X-linked Answer Key

X-linked inheritance is a pattern of inheritance in which genes are located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. X-linked genes are passed from parents to children through the X chromosome.
X-linked traits can be either dominant or recessive. A dominant X-linked trait will be expressed in individuals who have only one copy of the gene, while a recessive X-linked trait will only be expressed in individuals who have two copies of the gene.
The Role of the Y Chromosome in X-Linked Inheritance
The Y chromosome does not carry any X-linked genes. Therefore, males can only inherit X-linked genes from their mothers. Females can inherit X-linked genes from both their mothers and their fathers.
Punnett Squares for X-Linked Inheritance
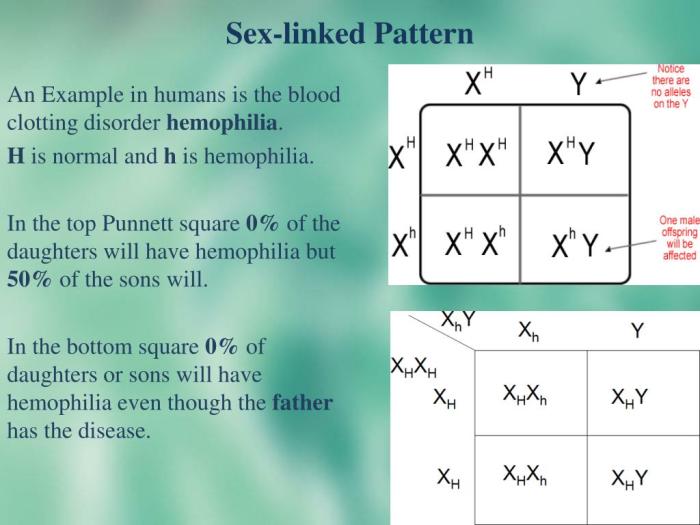
Punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting the probability of inheriting a particular trait. In the case of X-linked inheritance, Punnett squares can be used to determine the probability of a male or female inheriting a trait that is carried on the X chromosome.
To construct a Punnett square for X-linked inheritance, the genotype of the parents must be known. The genotype of a male is always XY, while the genotype of a female can be either XX or X aX a, where X arepresents the allele for the recessive trait.
Probability of Inheriting X-Linked Traits
The probability of inheriting an X-linked trait depends on the genotypes of the parents. If the father is affected by the trait, then all of his daughters will be carriers, and all of his sons will be affected. If the mother is affected by the trait, then all of her sons will be affected, and half of her daughters will be carriers.
If the mother is a carrier, then half of her sons will be affected, and half of her daughters will be carriers. If the father is not affected by the trait, then none of his children will be affected, but half of his daughters will be carriers.
Examples and Applications
X-linked traits are inherited in a specific pattern due to the presence of the X and Y chromosomes. Understanding these patterns is crucial in predicting the inheritance of X-linked disorders and providing genetic counseling.
Examples of X-linked traits include color blindness, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. These traits are more common in males than females because males only have one X chromosome, while females have two.
Using Punnett Squares to Predict Inheritance, Punnett squares x-linked answer key
Punnett squares are a valuable tool in predicting the inheritance of X-linked disorders. By analyzing the genotypes of the parents, we can determine the probability of a child inheriting the trait.
For example, if a father is colorblind (XcY) and the mother is a carrier (XCXc), the Punnett square shows that there is a 50% chance of their son being colorblind (XcY) and a 50% chance of their daughter being a carrier (XCXc).
Punnett Squares in Genetic Counseling
Punnett squares play a crucial role in genetic counseling, where they are used to inform families about the risks of inheriting genetic disorders.
By understanding the inheritance patterns of X-linked traits, genetic counselors can provide accurate information about the likelihood of a child being affected by a disorder. This information can help families make informed decisions about family planning and medical care.
Limitations and Considerations
While Punnett squares are a valuable tool for predicting inheritance patterns, they have certain limitations that must be considered. Understanding these limitations helps ensure accurate interpretations and appropriate use of Punnett squares.
One limitation is that Punnett squares assume independent assortment of alleles. However, in some cases, genes may be linked on the same chromosome, resulting in non-independent assortment. This can lead to deviations from the expected inheritance patterns predicted by Punnett squares.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
- Linkage:As mentioned above, linkage between genes can affect the accuracy of Punnett squares.
- Incomplete dominance:In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant over the other, resulting in an intermediate phenotype. Punnett squares cannot accurately predict the phenotype ratios in such cases.
- Codominance:In codominance, both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, leading to distinct phenotypes for heterozygous individuals. Punnett squares cannot predict the specific phenotypes in such cases.
- Multiple alleles:When a gene has more than two alleles, Punnett squares become more complex and may not accurately predict the inheritance patterns.
- Environmental factors:Environmental factors can influence the expression of genes, affecting the phenotype even when the genotype is known.
When to Use Punnett Squares
Punnett squares are most useful for predicting inheritance patterns in simple Mendelian traits, where the assumptions of independent assortment and complete dominance hold true. They can be a helpful tool for understanding the basic principles of inheritance and for predicting the probability of inheriting certain traits.
When to Seek Professional Genetic Counseling
In cases involving complex inheritance patterns, incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, or linkage, it is advisable to seek professional genetic counseling. Genetic counselors can provide personalized advice and interpret complex genetic information to help individuals make informed decisions about their health and reproductive choices.
Detailed FAQs
What are Punnett squares?
Punnett squares are diagrams that predict the possible genotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What is X-linked inheritance?
X-linked inheritance is a pattern of inheritance in which genes are located on the X chromosome.
How do I use Punnett squares to predict the inheritance of X-linked traits?
To use Punnett squares to predict the inheritance of X-linked traits, you need to know the genotypes of the parents.